The Files Analytics table displays detailed information about all files within your organization. This table allows you to easily track and inspect potentially harmful files and their associated users. In addition to monitoring, you can also implement effective remediation measures against risky files, preventing potential security damage.
The Files Forensics table displays the following information for each file:
-
File Name: The name of the file
-
Size: The size of the file
-
Last Edited: The date and time that the file was most recently edited
-
Owner: The owner of the file as defined in its properties
-
Folder: The folder in the drive in which the file is stored
-
DLP: Lists the number of data violations in the file. Data violations are Data Loss Prevention (DLP) rule matches.
-
Sharing: The file sharing level. In the case of an External file, lists the external domain name; in the case of an Externally owned file, lists the external domain name, if known. See File Sharing.
-
Cloud Service: The SaaS Application with which the alert is associated (for example, Google Workspace, Microsoft 365)
Viewing File Information
You can view additional information about each file by expanding the table entry.
The expanded area displays the following elements:
-
Sharing Details: Displays information about all users with permissions on this file. Indicates whether each user is an Owner, a Reader (has read permissions), or a Writer (has read-write permissions).
-
Recent Activity: Lists recent events relating to the file (for example, Download file, Edit file).
-
Data Security: Displays detailed information about sensitive data in the file detected by the system, defined as DLP matches. See Viewing Data Security Information.
-
File Manager (
 ): The remediation options for the file. See the following section.
): The remediation options for the file. See the following section. -
Status bar: Located at the bottom of the expanded area, the status bar displays detailed information about the file (time stamps for file creation and modification, file ID, and the folder containing the file).
You can view files and manually perform remediation on them.
Viewing Data Security Information
Proofpoint CASB searches for data violations: sensitive data found in files based on rules defined in the Data Loss Prevention (DLP) page . The system searches for Detectors based on selected Dictionary terms and Smart IDs.
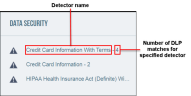
The DLP column in the Files Forensics table lists the number of times Detector values (DLP matches) occur in a file.
You can view details of the DLP matches in a file in the Data Security area of the expanded area in the Files Forensics table.
-
In the Files Forensics table, click the table entry of the selected file.
The Data Security area is located on the right side of the expanded area. Detectors found in the file are listed, along with the number of DLP matches in the file for the specified Detector. The total number of DLP matches in the Data Security area corresponds to the number of matches listed in the DLP column in the Files Forensics table.
-
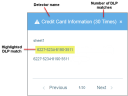
To view additional information, click a Detector name.
A window opens displaying a snippet from the file, highlighting one of the matched DLPs. The number of snippets available for viewing corresponds to the number of DLP matches for the specified Detector. You can scroll through the snippets to view each highlighted DLP match.
File Sharing
One of the key attributes of a file from a security perspective is sharing: who has ownership and read/write permissions for a file. The sharing attribute of a file, as displayed in the Files Forensics table, provides clear information about file accessibility.
The share level that is presented reflects the highest-risk, not the most permissive.
Sharing levels are defined as follows:
-
Private: The file is not shared with anyone. Only the owner has read/write permissions.
-
Internal: The file is shared with one or more users within the organization.
-
All [name of organization]: The file is shared with all users in the organization.
-
External: The file is shared with one or more users outside of the organization. Ownership outside your organization means you have no control over permissions, retention, or lifecycle. The external owner can change access settings at any time, potentially exposing sensitive data without your visibility. It can be harder to enforce DLP or governance policies because the file resides in another tenant.
-
Public: The file can be accessed by anyone. A public file is owned by your organization, so you can revoke access, apply DLP, and audit activity. You maintain control over the file and folder structure.
Publicly shared files are more risky because anyone with the link can access them.
-
Externally Owned: The file is owned by a user outside of the organization and shared with one or more users within the organization.
Unknown: Proofpoint CASB cannot evaluate the sharing level or determine with whom the file is being shared. (This is unusual; it occurs, for example, in Microsoft 365 if a file is owned by an application and so cannot be classified as external or internal.)